Species and habitats - Solea solea - Nurseries - Preferential habitat modellised by Generalised Linear Modelling from YFS survey
Simple
- Alternate title
- YFS_species_model
- Date ( Publication )
- 2009-12-31T10:57:00
- Identifier
- CHARM_SOLESOL_NURS_GLM_SIMPLE_MOD
- Other citation details
- Source CHARM Consortium
- Credit
- IFREMER / CEFAS, CHARM consortium
- Status
- Completed
- Maintenance and update frequency
- As needed
- Thèmes Sextant Thèmes Sextant ( Theme )
-
- /Biological Environment/Species/Fish Species of Commercial Interest
- Keywords ( Discipline )
-
- Sub-category
- nom variable FR
- Keywords ( Theme )
-
- Oceanographic geographical features
- GEMET - INSPIRE themes, version 1.0 GEMET - INSPIRE themes, version 1.0 ( Theme )
-
- Répartition des espèces
- Use limitation
- research-only
- Access constraints
- Other restrictions
- Use constraints
- License
- Other constraints
- Has to be cited this way in maps : "Source CHARM Consortium"
- Other constraints
- Has to be cited this way in bibliography : "Rochette, S., Rivot, E., Morin, J., Mackinson, S., Riou, P., Le Pape, O. (2010). Effect of nursery habitat degradation on flatfish population renewal. Application to Solea solea in the Eastern Channel (Western Europe). Journal of sea Research, Volume 64, p34-44. doi: 10.1016/j.seares.2009.08.003 , Open Access version : http://archimer.ifremer.fr/doc/00008/11921/.”
- Spatial representation type
- Grid
- Denominator
- 2500
- Metadata language
- en
- Metadata language
- fr
- Character set
- UTF8
- Topic category
-
- Oceans
- Biota
- Environment
- Environment description
- Microsoft Windows XP ; ESRI ArcGIS 9.x
- Geographic identifier
- Dover Strait and river Thames mouth
- Begin date
- 1977-01-01T11:08:00
- End date
- 2006-12-31T11:08:00
))
- Reference system identifier
- WGS 84 (EPSG:4326)
- Number of dimensions
- 0
- Cell geometry
- Area
- Transformation parameter availability
- No
Distributor
- OnLine resource
-
Charm web site
(
WWW:LINK
)
Charm web site
- OnLine resource
-
CHARMIII_SOLESOL_NURS_GLM_SIMPLE_MOD_PROB_PRED
(
OGC:WMS
)
Presence
- OnLine resource
-
CHARMIII_SOLESOL_NURS_GLM_SIMPLE_MOD_DENSITIES_PRED
(
OGC:WMS
)
Density
- OnLine resource
-
CHARMIII_SOLESOL_NURS_GLM_SIMPLE_MOD_LOGDENSITIES_PRED
(
OGC:WMS
)
LogDensity
- Protocol
- COPYFILE
- Name
- CHARMIII_SOLESOL_NURS_GLM_SIMPLE_MOD_PROB_PRED
- Description
- Presence
- Protocol
- COPYFILE
- Name
- CHARMIII_SOLESOL_NURS_GLM_SIMPLE_MOD_DENSITIES_PRED
- Description
- Density
- Protocol
- COPYFILE
- Name
- CHARMIII_SOLESOL_NURS_GLM_SIMPLE_MOD_LOGDENSITIES_PRED
- Description
- LogDensity
- Hierarchy level
- Dataset
Conformance result
- Date ( Creation )
- 2011-10-17
- Explanation
- INSPIRE related dataset
- Pass
- No
- Statement
- Combinations of the French YFS and the British YFS.
- Description
- GLM describes the mean response of a species abundance or presence probability according to environmental conditions (figure 2). In this type of model, a linear prediction is related to the mean of the response variable through a link function (e.g. identity function for a normally distributed variable, or logit function for binary data). Corresponding habitat models required a two step modelling procedure. The presence probability of the considered species as a function of environmental factors is first modelled using presence-absence data, independently from abundance data. Then, the response in terms of abundance is modelled in case of presence only. The species habitat can finally be predicted by combining the presence-absence model with the model of abundance response in case of presence. This procedure allows circumventing the problem of atypical distribution of count data which include numerous observations with value zero, which is common in species abundance data (Stefánsson, 1996; Barry & Welsh, 2002). In this study, model selection was carried out by initially fitting a complete model including different explanatory variables (note that interactions were not tested). The selected environment predictors were: Bathymetry and sediment structure a class factors. The GLM model was optimised through backward selection based on Chi-square or F-test significance tests (Venables & Ripley, 2002). This approach was taken rather than Akaike Information Criterion reduction (or AIC; Akaike, 1974). For presence-absence data, binomial modelling with logit link function was chosen to obtain a prediction of the probability of presence of the species considered. For non-null abundance data (i.e. removing zero values), the data was log-transformed to achieve normality, and gaussian modelling with identity link function was used to predict positive density on a log scale. The predicted probability of presence was then multiplied with the positive density prediction, to obtain the final predicted value of abundance (Stefánsson, 1996). For each species considered, the equation of the final habitat model was used to recode digital maps of the environmental factors with the predicted abundance (or presence probability) of the species, thereby producing a habitat map.
- Description
- FYFS + BYFS surveys
- File identifier
- d39e01f8-2132-461a-a708-af65da576061 XML
- Metadata language
- en
- Character set
- UTF8
- Hierarchy level
- Dataset
- Date stamp
- 2020-06-04T00:40:35
- Metadata standard name
- ISO 19115:2003/19139 - SEXTANT
- Metadata standard version
- 1.0
Overviews
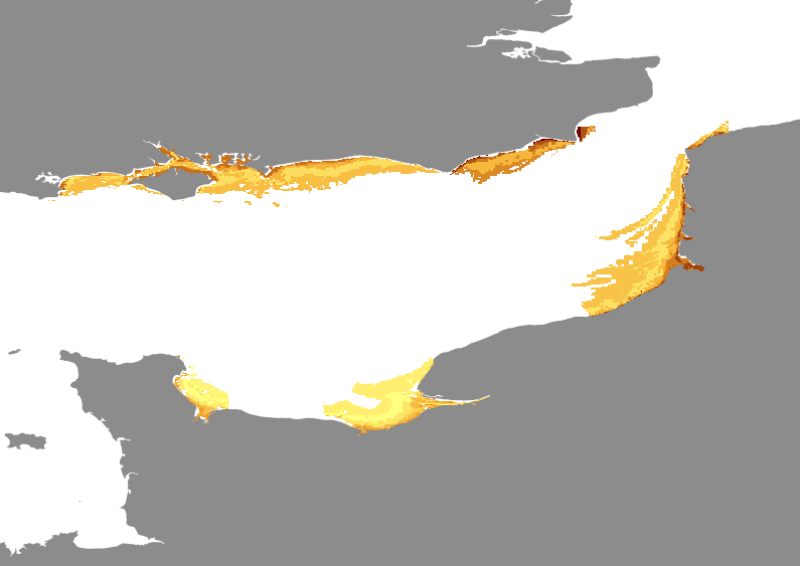
Spatial extent
))
Provided by

 Mon GéoSource
Mon GéoSource