D7: Hydrographical Conditions
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
INSPIRE themes
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-
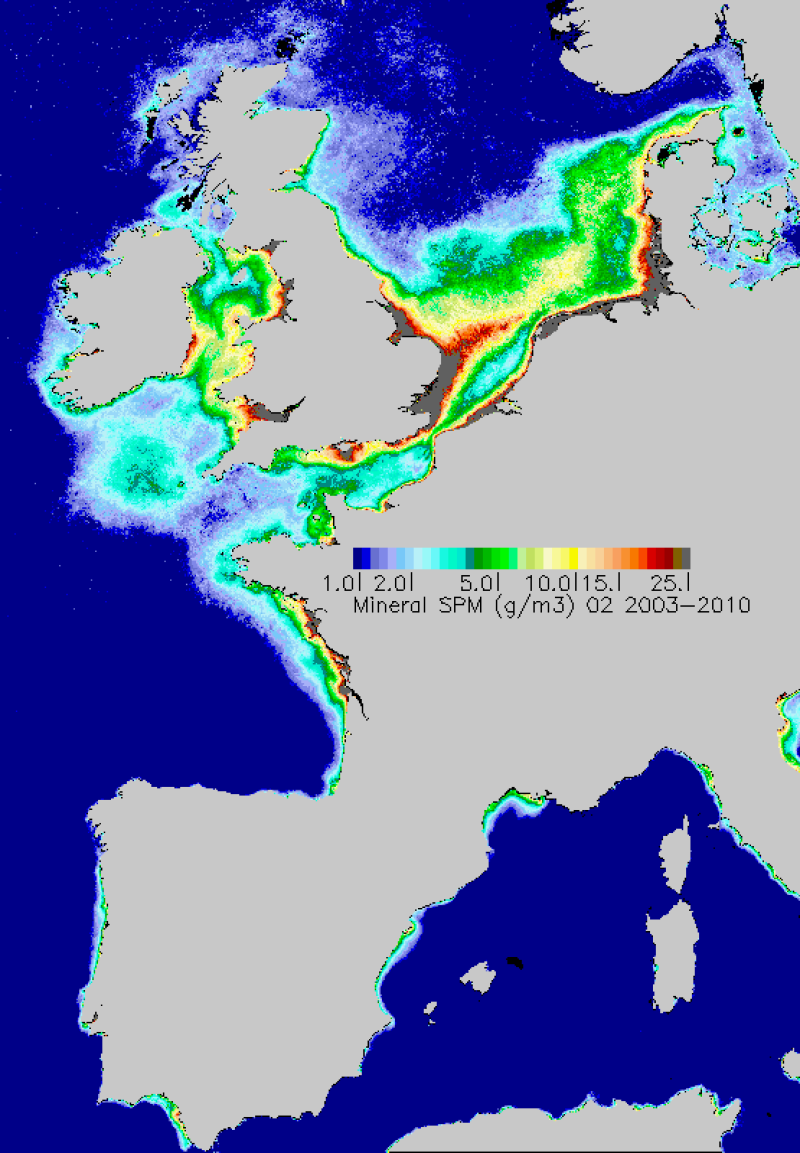
Map of average monthly non-algal suspended matter carried out in the period 2003-2010. TSS are estimated from the water reflectance using a specific algorithm developed at Ifremer.
-
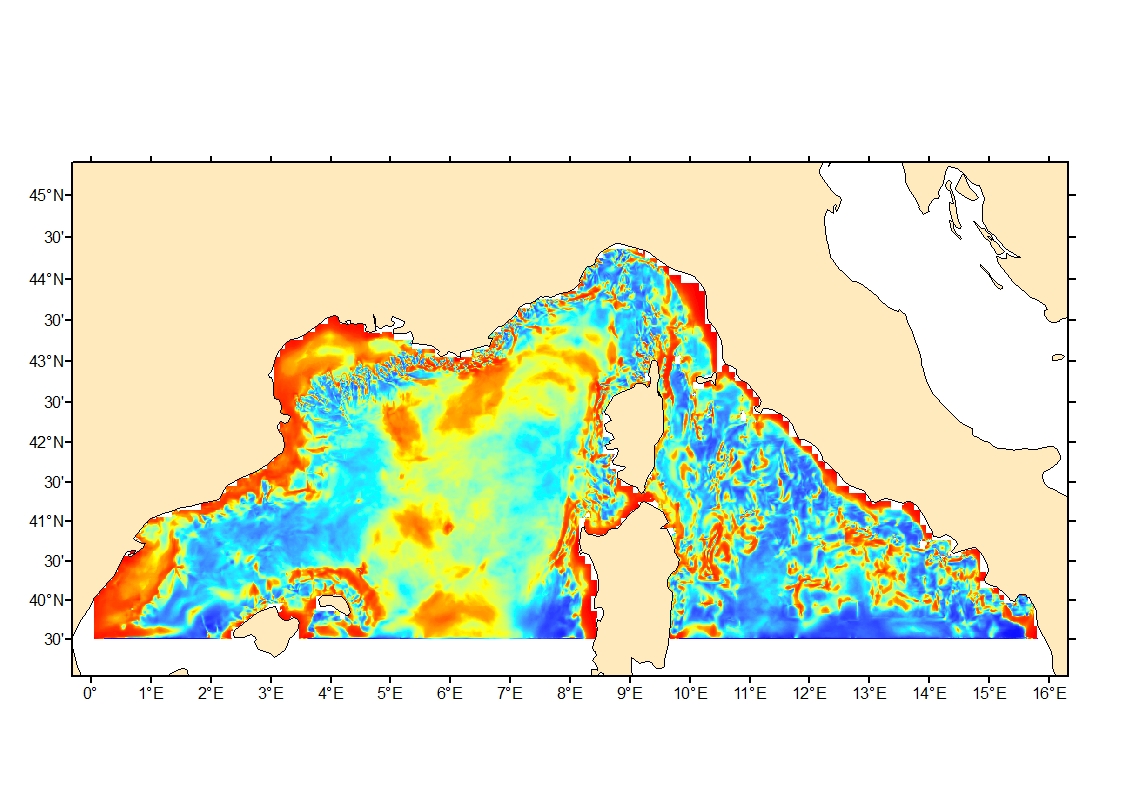
Seabed shear stress (in N.m-2) is a measure of the friction of water on the seabed due to waves and currents. The 90th percentile over the available period is used as layer for habitat models prediction.
-
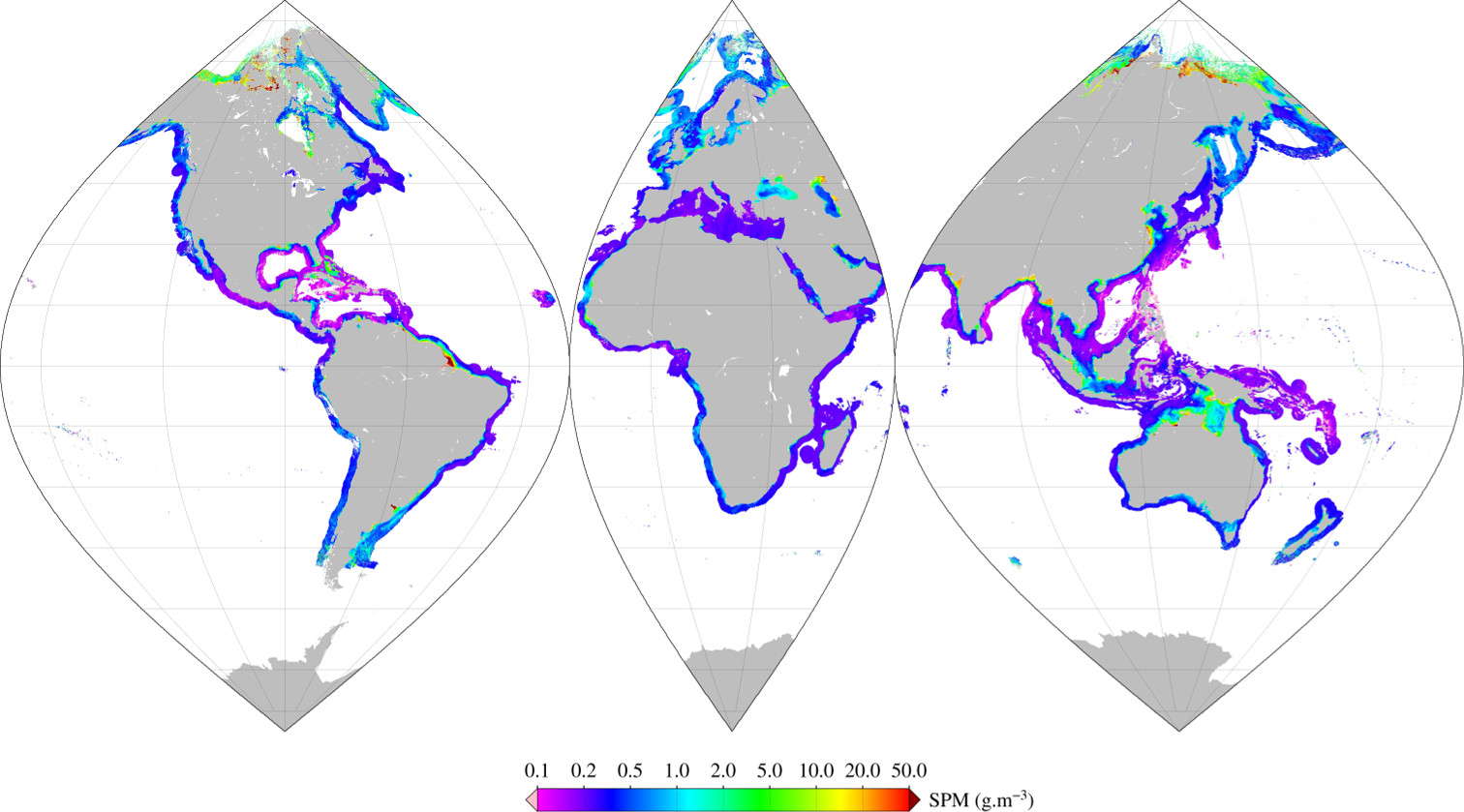
Monthly mean of Suspended Particulate Matter (2002-2012) using Han (2016) algorithm for coastal areas, at global scale, for MERIS sensor, with POLYMER atmospheric corrections. Ref: Bing Han, Hubert Loisel, Vincent Vantrepotte, Xavier Mériaux, Philippe Bryère,Sylvain Ouillon, David Dessailly, Qianguo Xing and Jianhua Zhu. Development of a Semi-Analytical Algorithm for the Retrieval of Suspended Particulate Matter rom Remote Sensing over Clear to Very Turbid Waters Remote Sens. 8, 211; doi:10.3390/rs8030211 2016
-
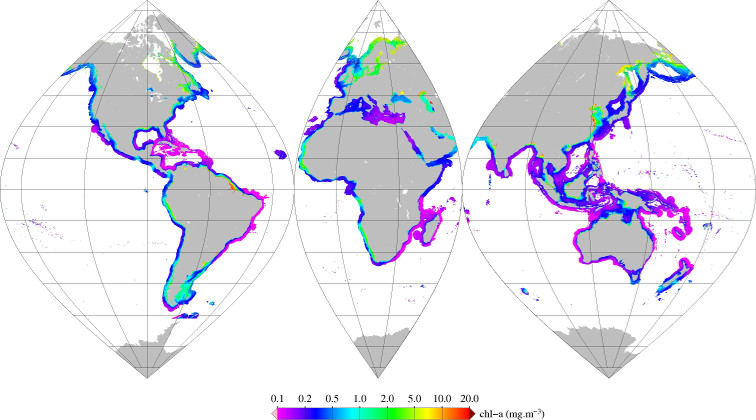
Monthly mean of chlorophyll-a (2002-2012) from Gohin (2002), for coastal areas, at global scale, for MERIS sensor, with POLYMER atmospheric corrections. Ref: F. Gohin , J. N. Druon & L. Lampert, A five channel chlorophyll concentration algorithm applied to SeaWiFS data processed by SeaDAS in coastal waters. IJRS Volume 23, 2002 - Issue 8 http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/01431160110071879 2002
-
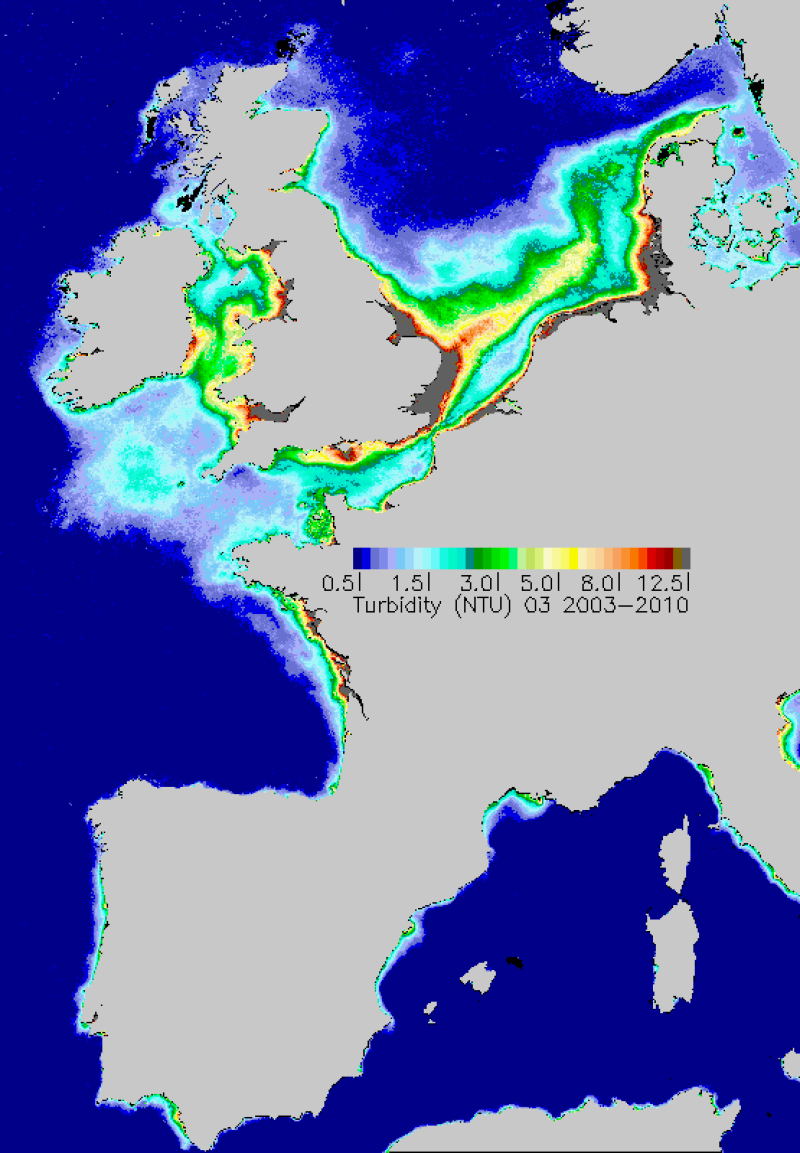
Average monthly turbidity maps made during the period 2003-2010. Turbidity is estimated from the concentrations of inorganic suspended materials and chlorophyll-a.
-
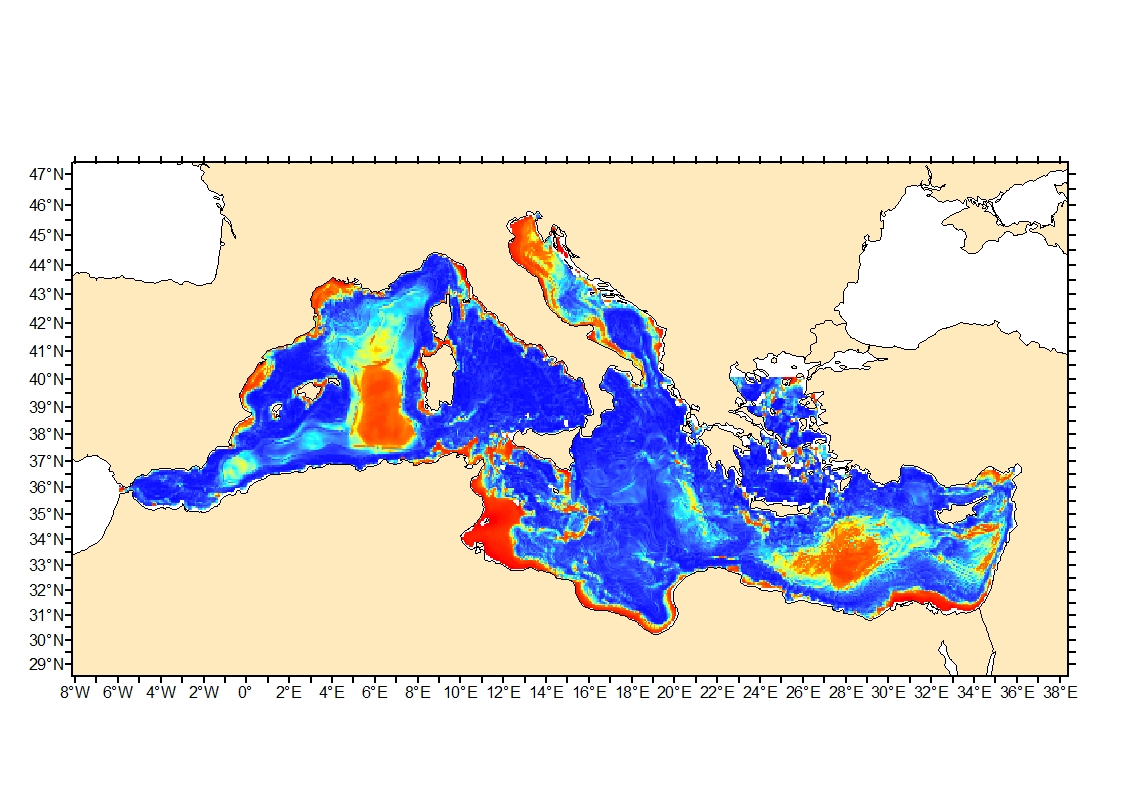
Seabed shear stress (in N.m-2) is a measure of the friction of water on the seabed due to waves and currents. The 90th percentile over the available period is used as layer for habitat models prediction.
 Mon GéoSource
Mon GéoSource