Celtic Seas
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
INSPIRE themes
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-
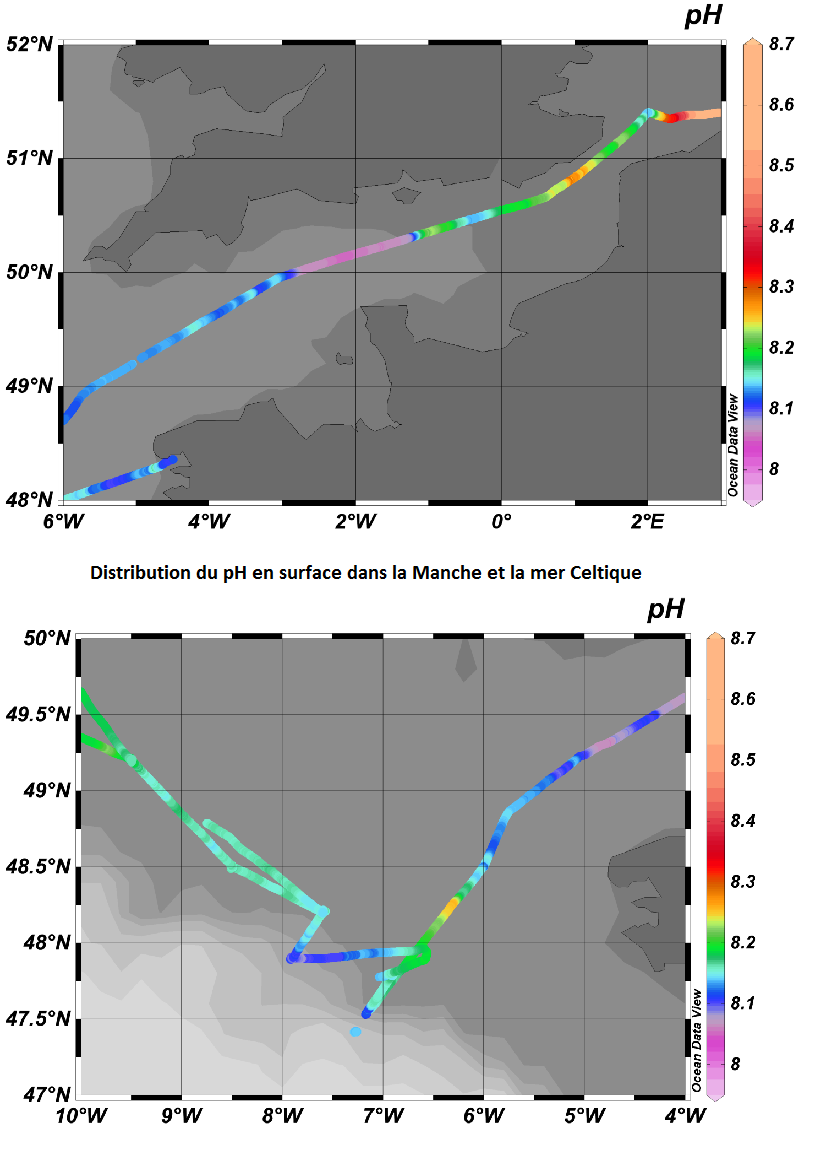
-
The chemical status of a coastal water body (coastal water or transition water) is determined by the most declassing of the defined states for heavy metals, pesticides, industrial pollutants and other pollutants taken into account by the WFD . The assessment is done once per management plan (once every six years). The most recent assessment of the state of the chemical state is presented in the DCE Loire-Bretagne atlas. Earlier reports are available in annual archives.
-
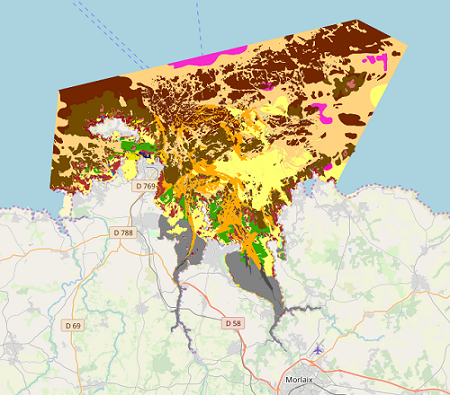
Map of benthic habitat synthesis of the Natura 2000 site FR5300015 - Bay of Morlaix is the result of the fusion and harmonization of five cartographic data. They were generated according to mapping strategies, interpretation scales and on the basis of different cartographic supports.
-
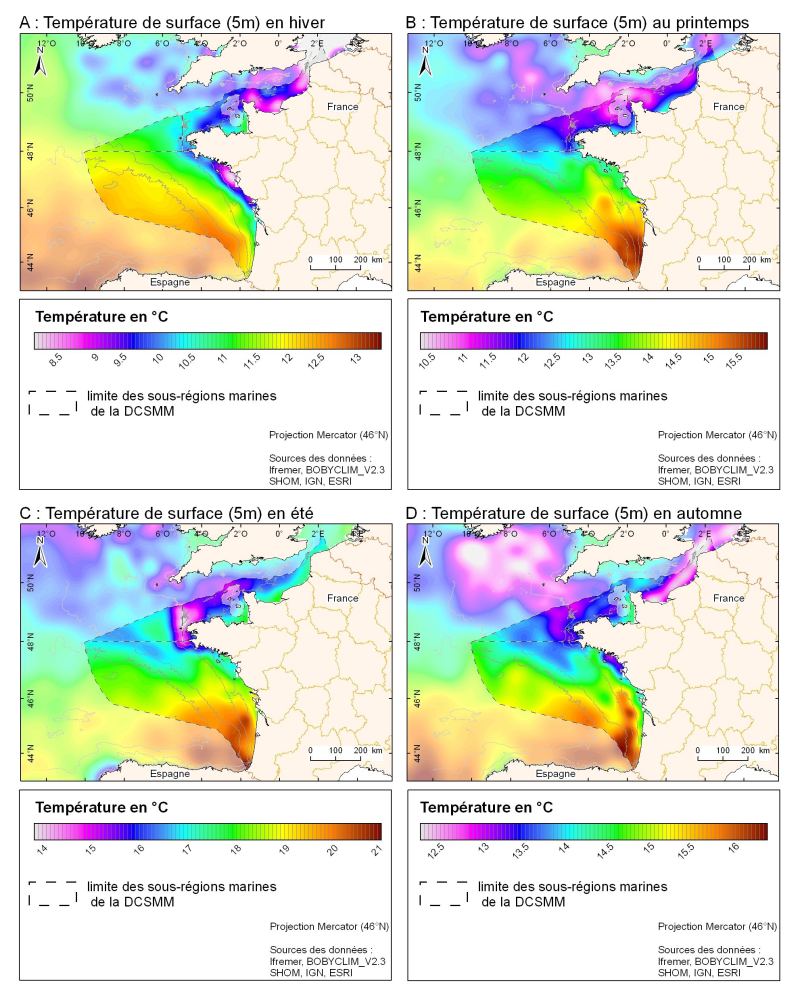
3D seasonal temperature range (in ° C) obtained by objective analysis (interpolation) of the raw data in situ, at a depth of 5m. Within the Bay of Biscay Challenge and the programme of the Operational Coastal Oceanographic Centre Prévimer, the services of SISMER DYNECO-PHYSED of IFREMER have built a joint hydrological database of the Bay of Biscay, from CTD measurements, Bouteilles, XBT / MBT and Profileurs from multiple global data centres to achieve a climatological atlas of the region for temperature and salinity.
-
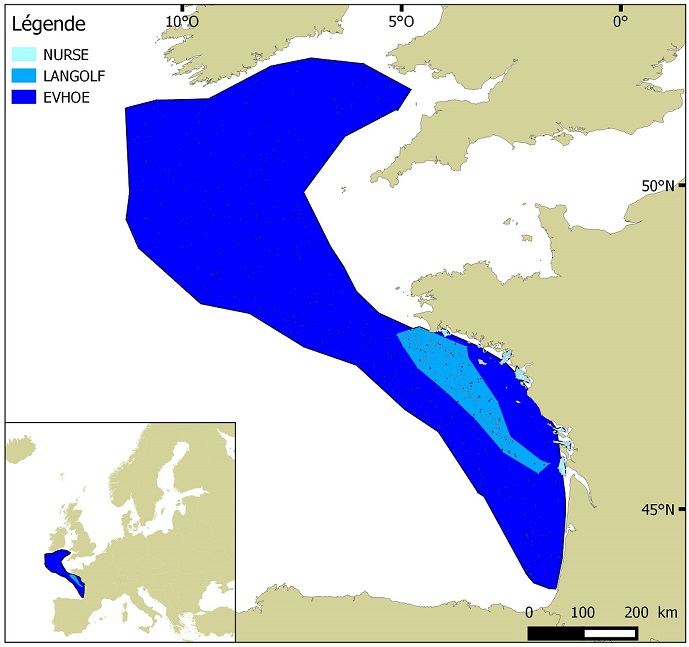
Distribution of benthic invertebrate species in Atlantic based on cumulative and interpolated relative abundance density data from fisheries surveys EVHOE (2008-2013), LANGOLF (2011-2013), NURSE (2000-2013), ORHAGO (2011-2015)
-
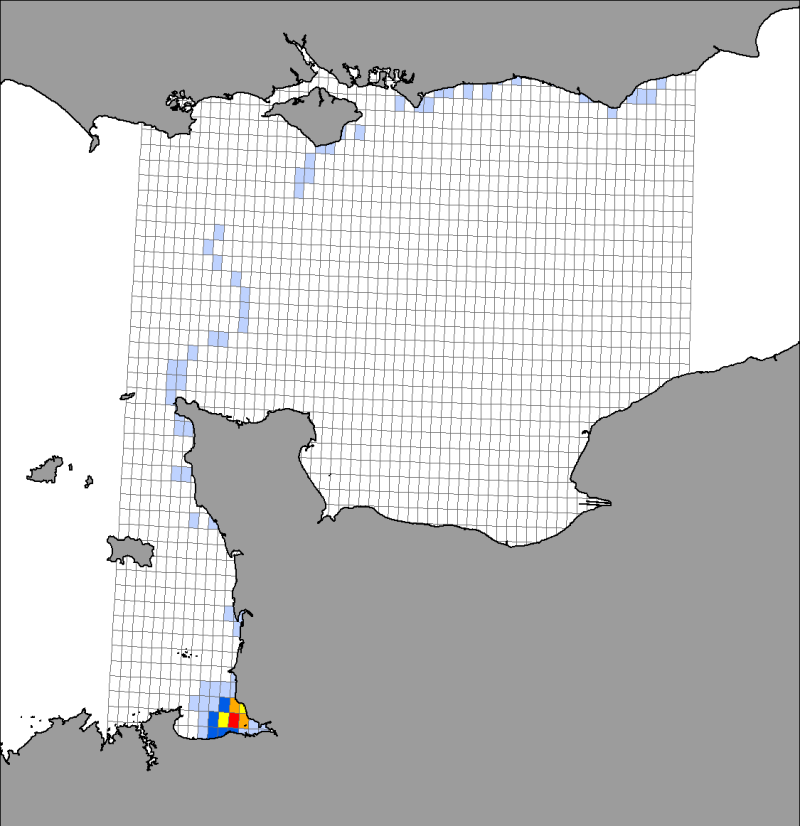
Location distribution per grid cell of 8 harbor seals (Phoca vitulina), followed by Fastloc GPS / GSM tags from the bay of Mont Saint-Michel from 2006 to 2008
-
-
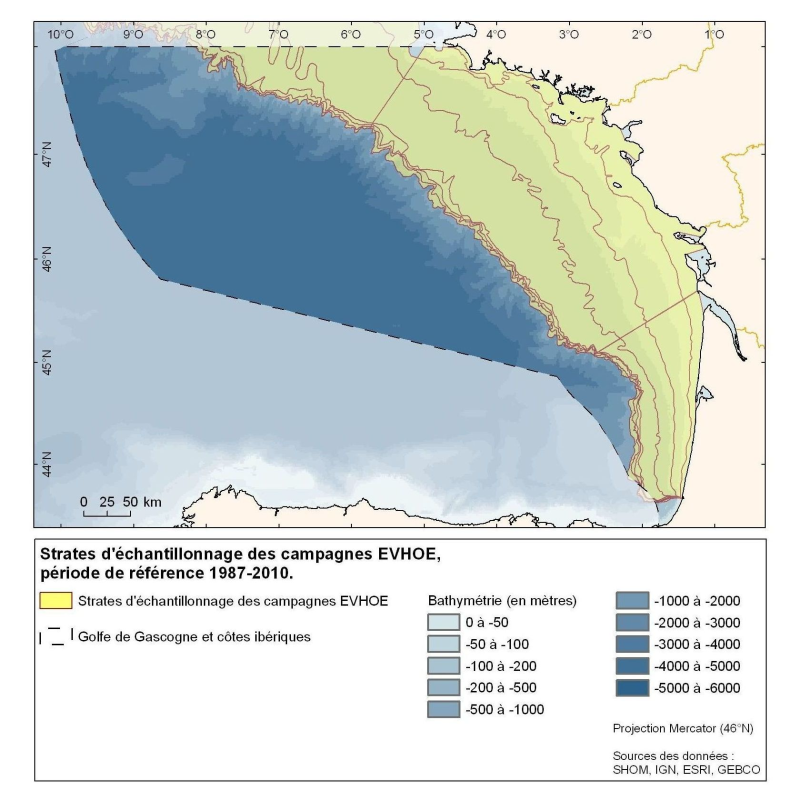
Polygons defined for the distribution of the sampling points of the EVHOE (Evaluation of Fish Stocks in Western Europe) campaigns in the Bay of Biscay and the Celtic Sea.
-
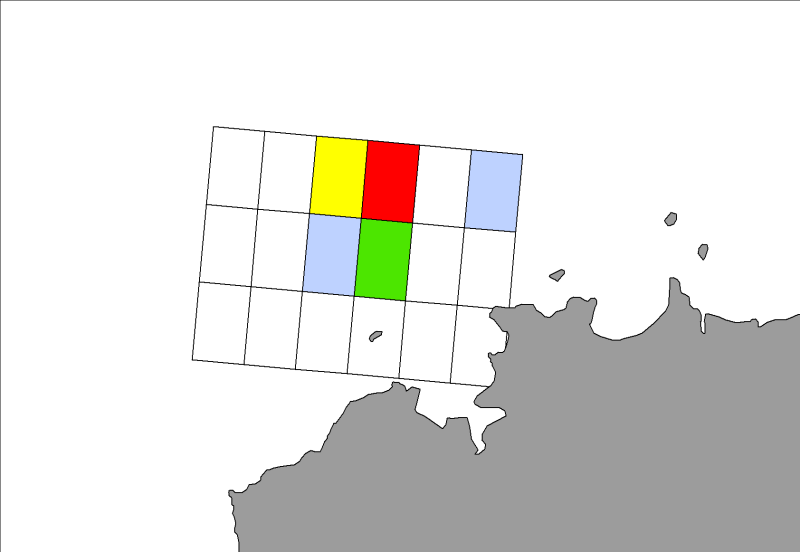
Seasonal spatial distribution of gray seals (Halichoerus grypus) on their haul out sites identified by the ONCFS on the rocks of Portsall in 2010.
-
The analysis concerns the assessment of the overall state of the coastal and transitional waters of the Western Channel and the Bay of Biscay. It results from the combination of the ecological status and the chemical status of each water body according to the rules of the European Water Framework Directive (WFD). The most recent assessment of the state is presented in the DCE Loire-Bretagne atlas. Earlier reports are available in annual archives.
 Mon GéoSource
Mon GéoSource