Environment
Type of resources
Available actions
INSPIRE themes
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-
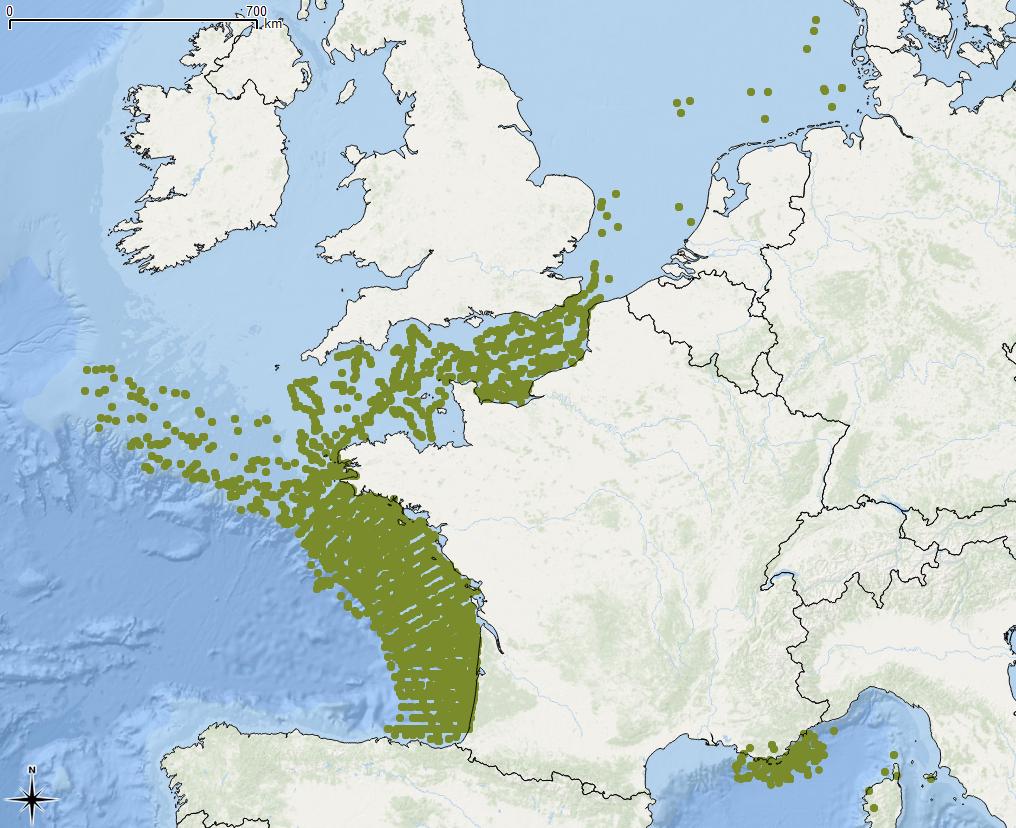
Quantité et localisation des déchets flottants observés, en Manche/Atlantique, suivant le protocole MEGASCOPE développé par l’UMS-PELAGIS lors des campagnes halieutiques mises en œuvre par l’Ifremer : IBTS, PELGAS, MEDITS, CGFS, EVHOE ; en Méditerranée par l’Institut ECOOcean et l’association Participe Futur. L’Evaluation 2018 de la DCSMM traite les données sur la période 2010-2016.
-
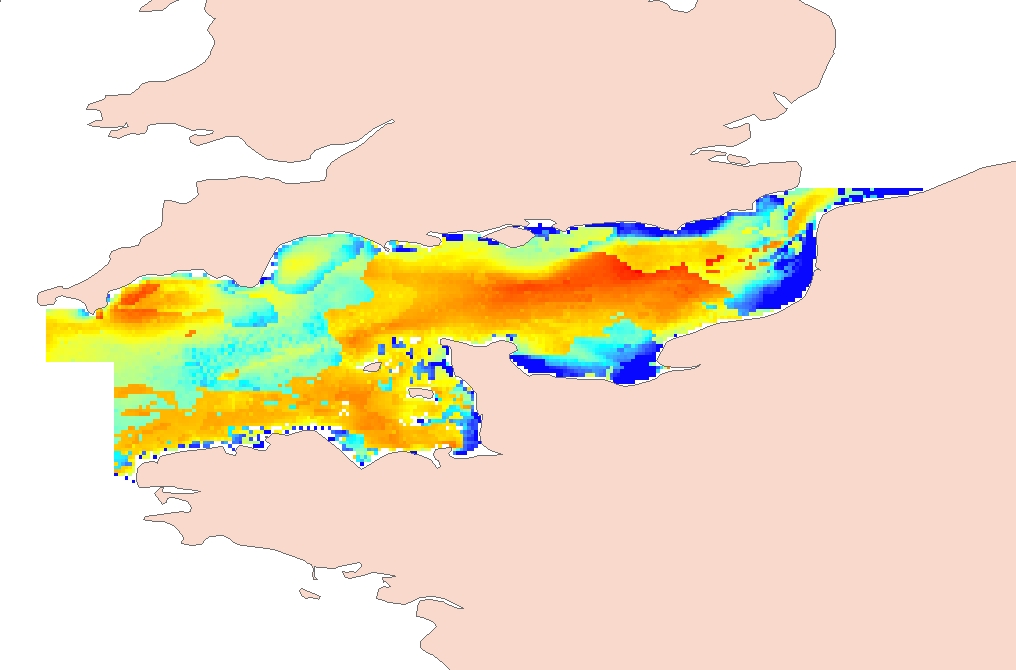
Process-driven seafloor habitat sensitivity (PDS) has been defined from the method developed by Kostylev and Hannah (2007), which takes into account physical disturbances and food availability as structuring factors for benthic communities. It is a conceptual model, relating species’ life history traits to environmental properties. Physical environment maps have been converted into a map of benthic habitat types, each supporting species communities with specific sensitivity to human pressures. It is based on two axes of selected environmental forces. The "Disturbance" (Dist) axis reflects the magnitude of change (destruction) of habitats (i.e. the stability through time of habitats), only due to natural processes influencing the seabed and which are responsible for the selection of life history traits. The "Scope for Growth" (SfG) axis takes into account environmental stresses inducing a physiological cost to organisms and limiting their growth and reproduction potential. This axis estimates the remaining energy available for growth and reproduction of a species (the energy spent on adapting itself to the environment being already taken into account). It can be related to the metabolic theory of the ecology. The process-driven sensitivity (PDS) can be seen as a risk map that combines the two previous axes and reflects the main ecological characteristics of the benthic habitats regarding natural processes. Areas with low disturbance are areas with a naturally low reworking of the sediment, allowing the establishment of a rich sessile epifauna community, with K-strategy species. Areas with low SfG means that the environmental factors, even though there are not limiting, are in lower values, i.e. that it imposes a cost for species to live. In areas combining low disturbance and low SfG, big suspension-feeder species with long life and slow growth can often be found: these species are more vulnerable in case of added disturbance. Details may be found in Foveau A, Vaz S, Desroy N, Kostylev VE (2017) Process-driven and biological characterisation and mapping of seabed habitats sensitive to trawling. PLoS ONE 12(10): e0184486. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0184486
-
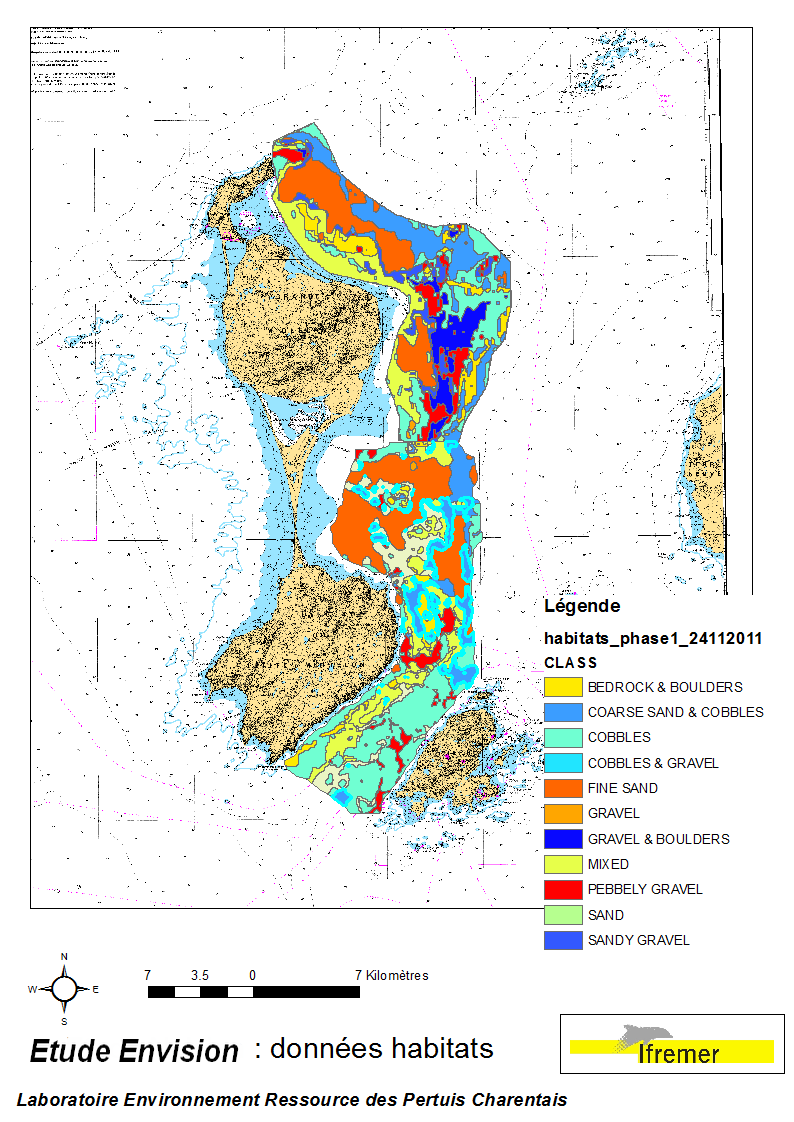
Ces données ont été acquises lors des campagnes Envision-Ifremer en 2007 et 2011, dans le cadre d'un projet de contribution au développement de la filière aquacole avec le soutien de l'ODEADOM et du Conseil Territorial de St Pierre et Miquelon. L’objectif de ce travail est le traitement des informations issues des deux campagnes de cartographie des fonds réalisées en 2007 et 2011 sur la côte est de St Pierre & Miquelon afin d’évaluer de nouvelle zones de semis potentiels de pétoncle géant (Placopecten magellanicus) et d’estimer les productions potentielles de ces zones.
-
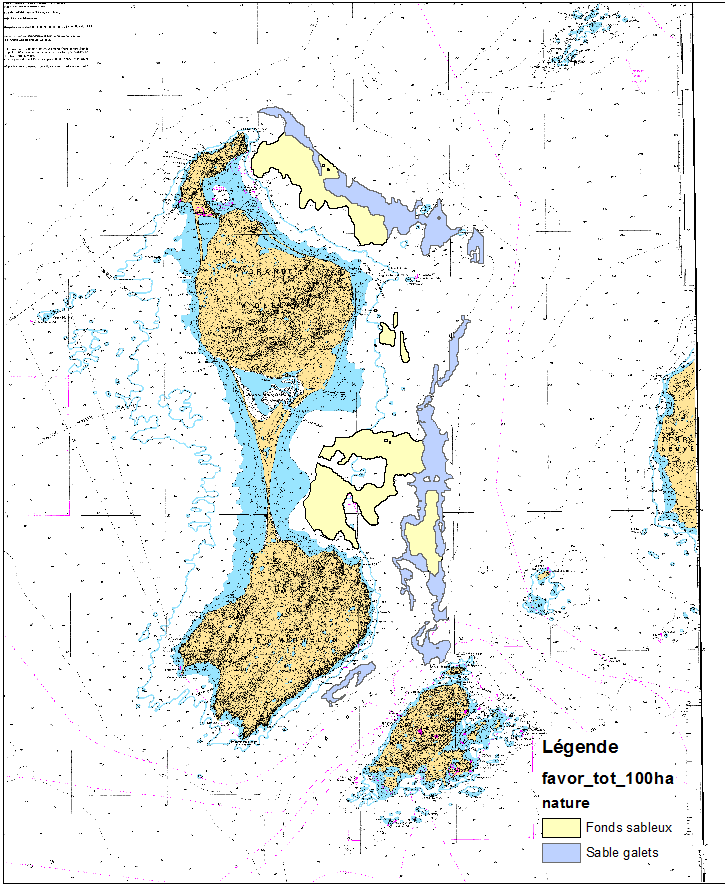
Ces données ont été acquises lors des campagnes Envision-Ifremer en 2007 et 2011, dans le cadre d'un projet de contribution au développement de la filière aquacole avec le soutien de l'ODEADOM et du Conseil Territorial de St Pierre et Miquelon. Zones favorables et exploitables au développement de la filière aquacole sur la côte Est de Saint-Pierre-et-Miquelon
-
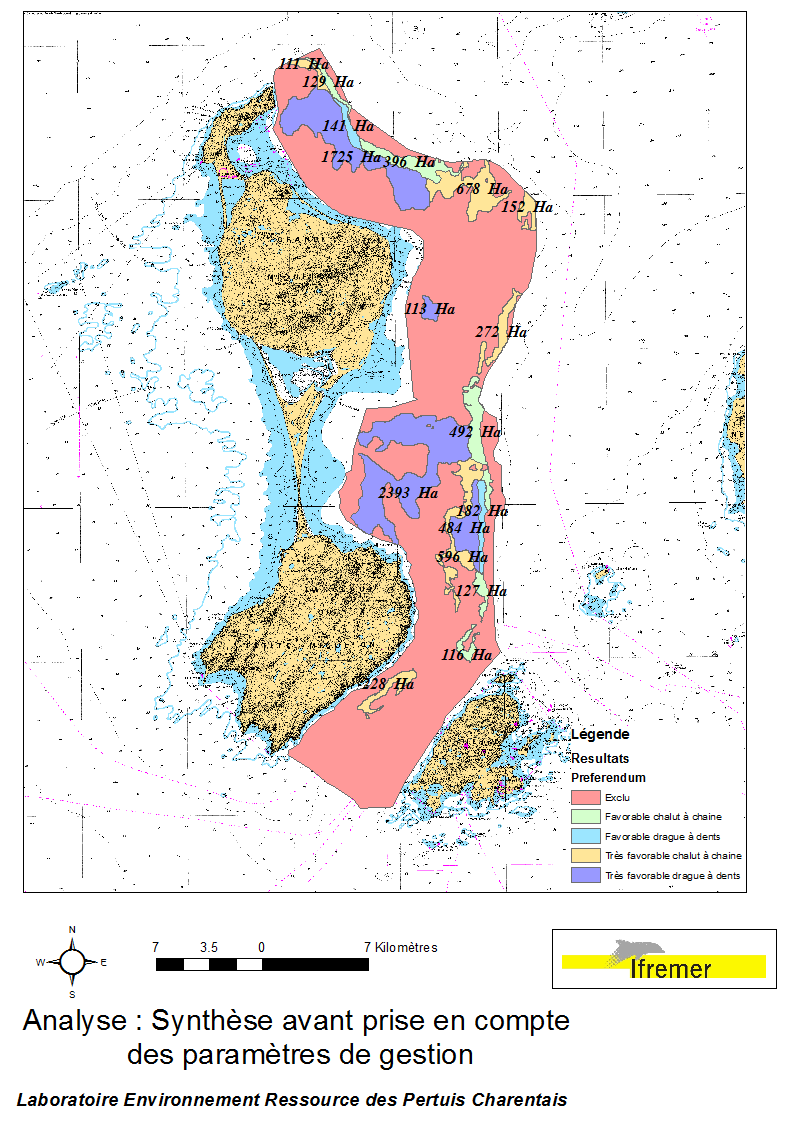
Ces données ont été acquises lors des campagnes Envision-Ifremer en 2007 et 2011, dans le cadre d'un projet de contribution au développement de la filière aquacole avec le soutien de l'ODEADOM et du Conseil Territorial de St Pierre et Miquelon. Synthèse de l'analyse spatialisée multicritères des superficies potentiellement exploitables par des semis contrôlés de pétoncles géants Placopecten magellanicus, sur la côte Est de l’île de Miquelon.
-
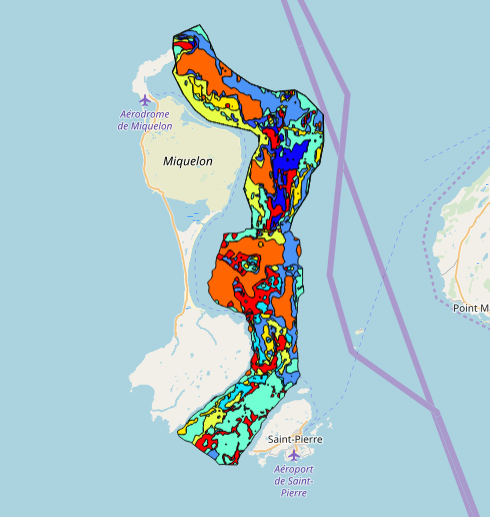
Ces données ont été acquises lors des campagnes Envision-Ifremer en 2007 et 2011, dans le cadre d'un projet de contribution au développement de la filière aquacole avec le soutien de l'ODEADOM et du Conseil Territorial de St Pierre et Miquelon. L’objectif de ce travail est le traitement des informations issues des deux campagnes de cartographie des fonds réalisées en 2007 et 2011 sur la côte est de St Pierre & Miquelon afin d’évaluer de nouvelle zones de semis potentiels de pétoncle géant (Placopecten magellanicus) et d’estimer les productions potentielles de ces zones.
-
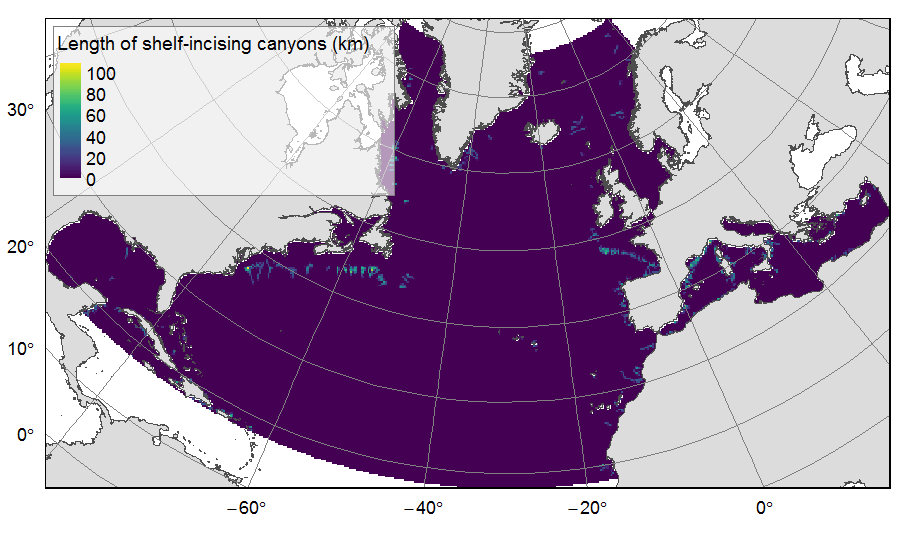
Distribution of three geomorphologic features (fracture zones, canyons, and seamounts) on the North Atlantic (18°N to 76°N and 36°E to 98°W). Source vector data originated from the GEBCO Gazetteer of Undersea Features Names for fractures, Harris & Whiteway (2011) for canyons, and Yesson et al. (2011) for seamounts. The presence (value=1) of fracture zones or seamounts and the total length of canyons (in km, independently for shelf-incising or blind canyons) was extracted in 25km * 25km gridsquares. This dataset was built to feed a basin-wide spatial conservation planning exercise, targeting the deep sea of the North Atlantic. The goal of this approach was to identify conservation priority areas for Vulnerable Marine Ecosystems (VMEs) and deep fish species, based on the distribution of species and habitats, human activities and current spatial management.
-
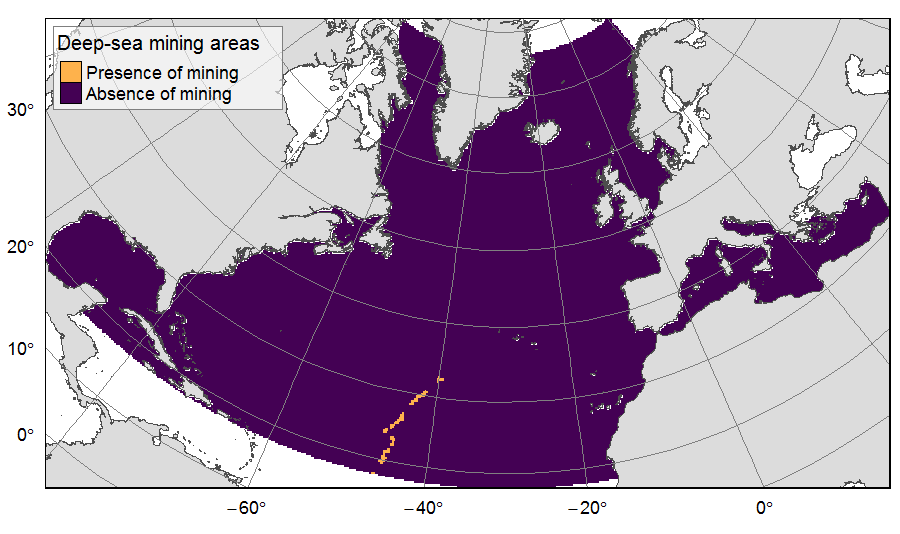
Presence of deep-sea mining exploration zones on the North Atlantic (18°N to 76°N and 36°E to 98°W). These areas correspond to the three polymetallic sulphides exploration contracts on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, attributed to Poland, France and Russia. Each of the three contract areas is divided into 100 squares of 10km by 10km. Source polygons originated from the International Seabed Authority. The presence (value=1) of deep-sea mining was extracted in 25km * 25km gridsquares. This dataset was built to feed a basin-wide spatial conservation planning exercise, targeting the deep sea of the North Atlantic. The goal of this approach was to identify conservation priority areas for Vulnerable Marine Ecosystems (VMEs) and deep fish species, based on the distribution of species and habitats, human activities and current spatial management.
-
La cartographie des habitats au large du Congo a été réalisée par le laboratoire Environnement Profond de l'Ifremer dans le cadre du projet ANR CONGOLOBE (2011-2015, responsable Christophe RABOUILLE). La méthode employée pour cette cartographie des habitats repose sur le dépouillement préalable des images acquises grâce au ROV Victor 6000 dans le cadre de deux campagnes océanographiques : WACS (du 26/01/2011 au 25/02/2011, chef de mission : Karine OLU) et CONGOLOBE (du 11/12/2011 au 12/01/2012, chef de mission : Christophe RABOUILLE). Les habitats ont été décrits au plus fin niveau d'analyse puis ont été classifiés selon la typologie EUNIS (https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/data/eunis-habitat-classification-1). Données publiées dans: Sen, A., B. Dennielou, J. Tourolle, A. Arnaubec, C. Rabouille and K. Olu (2017). Fauna and habitat types driven by turbidity currents in the lobe complex of the Congo deep-sea fan. Deep-Sea Research Part Ii-Topical Studies in Oceanography 142: 167-179. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr2.2017.05.009
-

LOCALISATION : sde.orn.sde_spc et sde.orn.sde_trspc --- ANNÉE : 2009 --- FORMAT : vecteur --- DÉTAIL : - BD Carthage 2008 - IGN, - Données des SPC Méditerranee-Ouest, SPC Grand Delta et SPC Tarn-Lot - Limites communales et départementales - BD Carto IGN - Localisation des cours d'eau bénéficiant d'un suivi en cas de crues (tronçons réglemantaires) et des stations SPC
 Mon GéoSource
Mon GéoSource