Environment
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
INSPIRE themes
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-
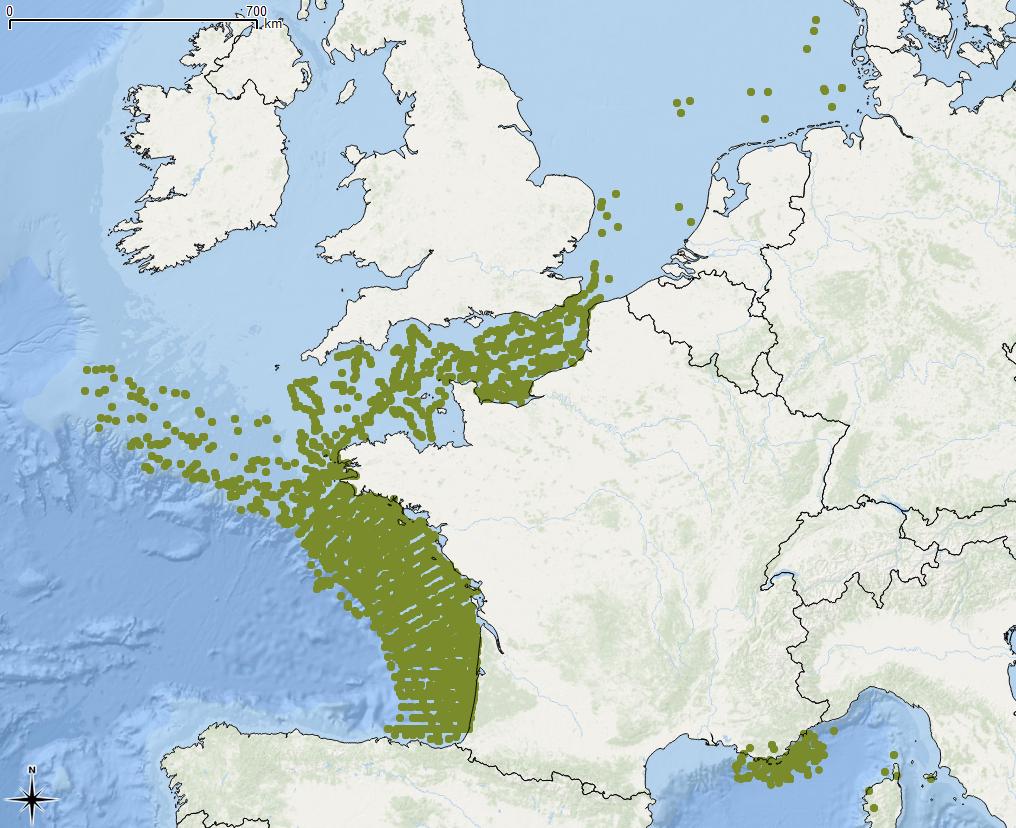
-
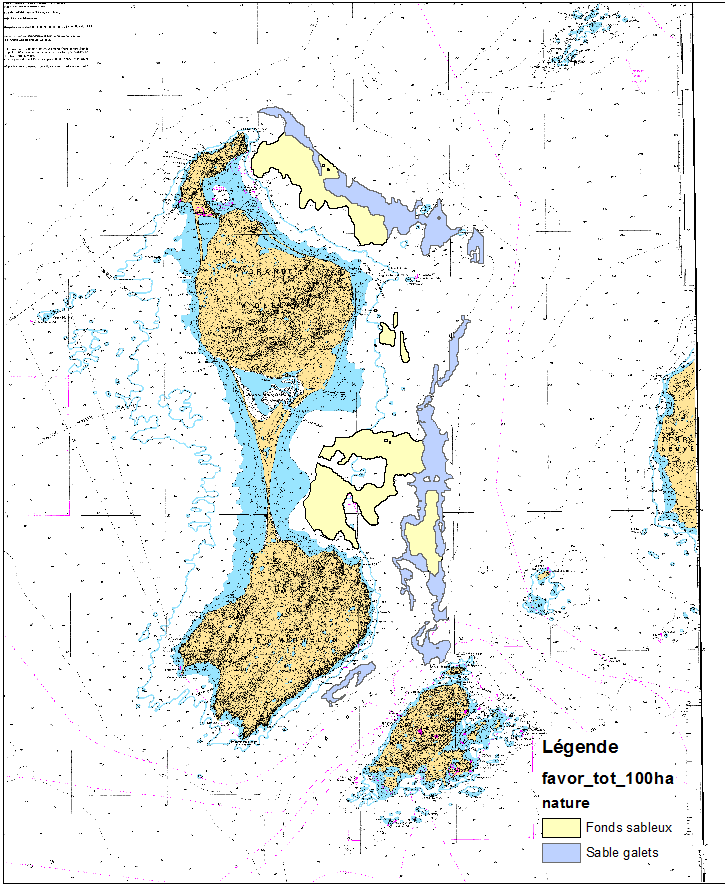
This data set was obtained during 2 ENVISION-IFREMER field campaigns carried out in 2007 and 2011 to sustain a Pectinid aquaculture project. This project was co-funded by ODEADOM and the public collectivity of Saint Pierre et Miquelon. Potential areas for further aquaculture exploitation and development on the Eastern coast of Saint Pierre et Miquelon.
-
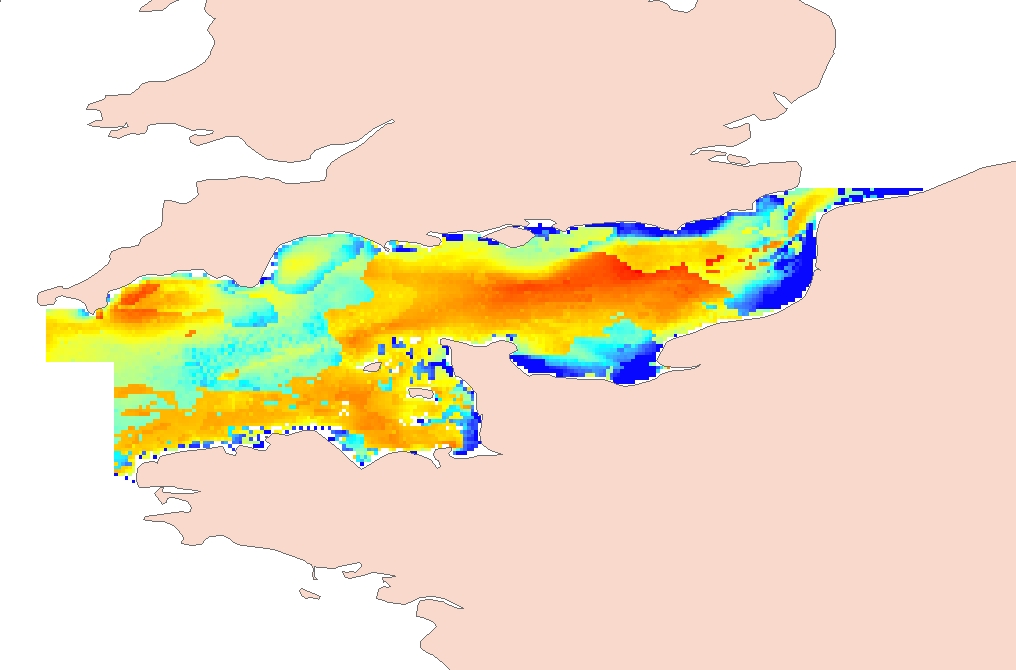
Process-driven seafloor habitat sensitivity (PDS) has been defined from the method developed by Kostylev and Hannah (2007), which takes into account physical disturbances and food availability as structuring factors for benthic communities. It is a conceptual model, relating species’ life history traits to environmental properties. Physical environment maps have been converted into a map of benthic habitat types, each supporting species communities with specific sensitivity to human pressures. It is based on two axes of selected environmental forces. The "Disturbance" (Dist) axis reflects the magnitude of change (destruction) of habitats (i.e. the stability through time of habitats), only due to natural processes influencing the seabed and which are responsible for the selection of life history traits. The "Scope for Growth" (SfG) axis takes into account environmental stresses inducing a physiological cost to organisms and limiting their growth and reproduction potential. This axis estimates the remaining energy available for growth and reproduction of a species (the energy spent on adapting itself to the environment being already taken into account). It can be related to the metabolic theory of the ecology. The process-driven sensitivity (PDS) can be seen as a risk map that combines the two previous axes and reflects the main ecological characteristics of the benthic habitats regarding natural processes. Areas with low disturbance are areas with a naturally low reworking of the sediment, allowing the establishment of a rich sessile epifauna community, with K-strategy species. Areas with low SfG means that the environmental factors, even though there are not limiting, are in lower values, i.e. that it imposes a cost for species to live. In areas combining low disturbance and low SfG, big suspension-feeder species with long life and slow growth can often be found: these species are more vulnerable in case of added disturbance. Details may be found in Foveau A, Vaz S, Desroy N, Kostylev VE (2017) Process-driven and biological characterisation and mapping of seabed habitats sensitive to trawling. PLoS ONE 12(10): e0184486. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0184486
-

LOCALISATION : sde.orn.sde_spc et sde.orn.sde_trspc --- ANNÉE : 2009 --- FORMAT : vecteur --- DÉTAIL : - BD Carthage 2008 - IGN, - Données des SPC Méditerranee-Ouest, SPC Grand Delta et SPC Tarn-Lot - Limites communales et départementales - BD Carto IGN - Localisation des cours d'eau bénéficiant d'un suivi en cas de crues (tronçons réglemantaires) et des stations SPC
-
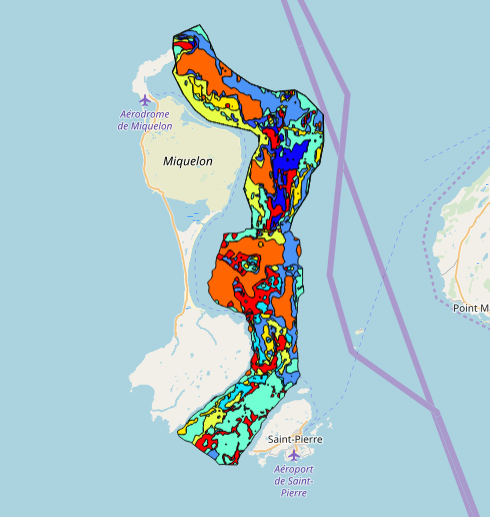
This data set was collected during 2 ENVISION-IFREMER field campaigns carried out in 2007 and 2011 to sustain a Pectinid aquaculture project. This was co-funded by ODEADOM and the public collectivity of Saint Pierre et Miquelon. This work aims to assess new seeding and rearing areas for the King scallop Placopecten magellanicus through a site selection process using the bottom type mapping data set obtained during the 2 ENVISION-IFREMER field campaigns. Furthermore, new estimates of potental scallop production is produced by this data treatment.
-
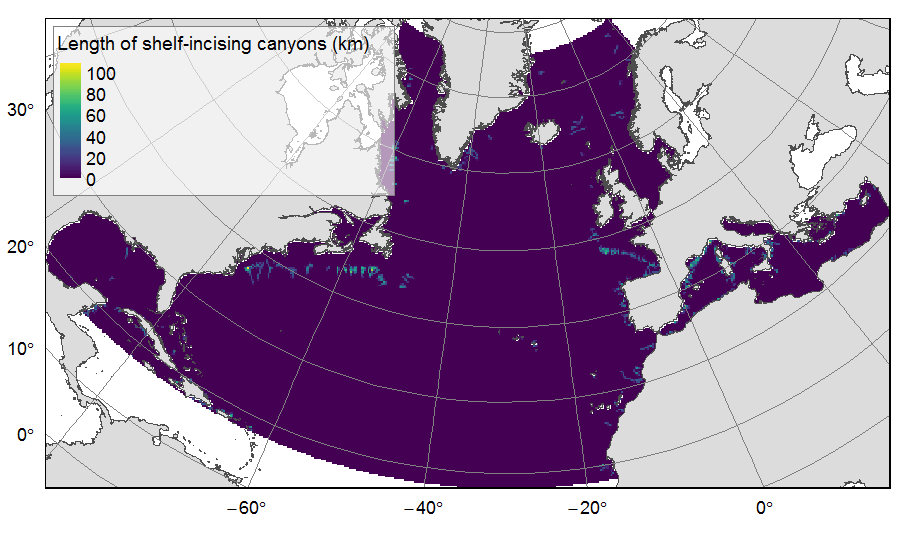
Distribution of three geomorphologic features (fracture zones, canyons, and seamounts) on the North Atlantic (18°N to 76°N and 36°E to 98°W). Source vector data originated from the GEBCO Gazetteer of Undersea Features Names for fractures, Harris & Whiteway (2011) for canyons, and Yesson et al. (2011) for seamounts. The presence (value=1) of fracture zones or seamounts and the total length of canyons (in km, independently for shelf-incising or blind canyons) was extracted in 25km * 25km gridsquares. This dataset was built to feed a basin-wide spatial conservation planning exercise, targeting the deep sea of the North Atlantic. The goal of this approach was to identify conservation priority areas for Vulnerable Marine Ecosystems (VMEs) and deep fish species, based on the distribution of species and habitats, human activities and current spatial management.
-
The mapping of pockmark habitats (cold fluid emissions) off the coast of Congo was carried out by Ifremer's Deep-Sea Laboratory as part of the WACS cruise. The method used for this habitat mapping is based on the preliminary analysis of videos acquired with the ROV Victor 6000 during the oceanographic cruise: WACS (from 26/01/2011 to 25/02/2011, mission leader: Karine OLU). The habitats were described at the finest level of analysis and then classified according to the EUNIS typology (https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/data/eunis-habitat-classification-1). Data published in: Marcon, Y., H. Sahling, A.-G. Allais, G. Bohrmann and K. Olu (2014a). Distribution and temporal variation of mega-fauna at the Regab pockmark (Northern Congo Fan), based on a comparison of videomosaics and geographic information systems analyses." Marine Ecology 35(1): 77-95. doi: 10.1111/maec.12056
-
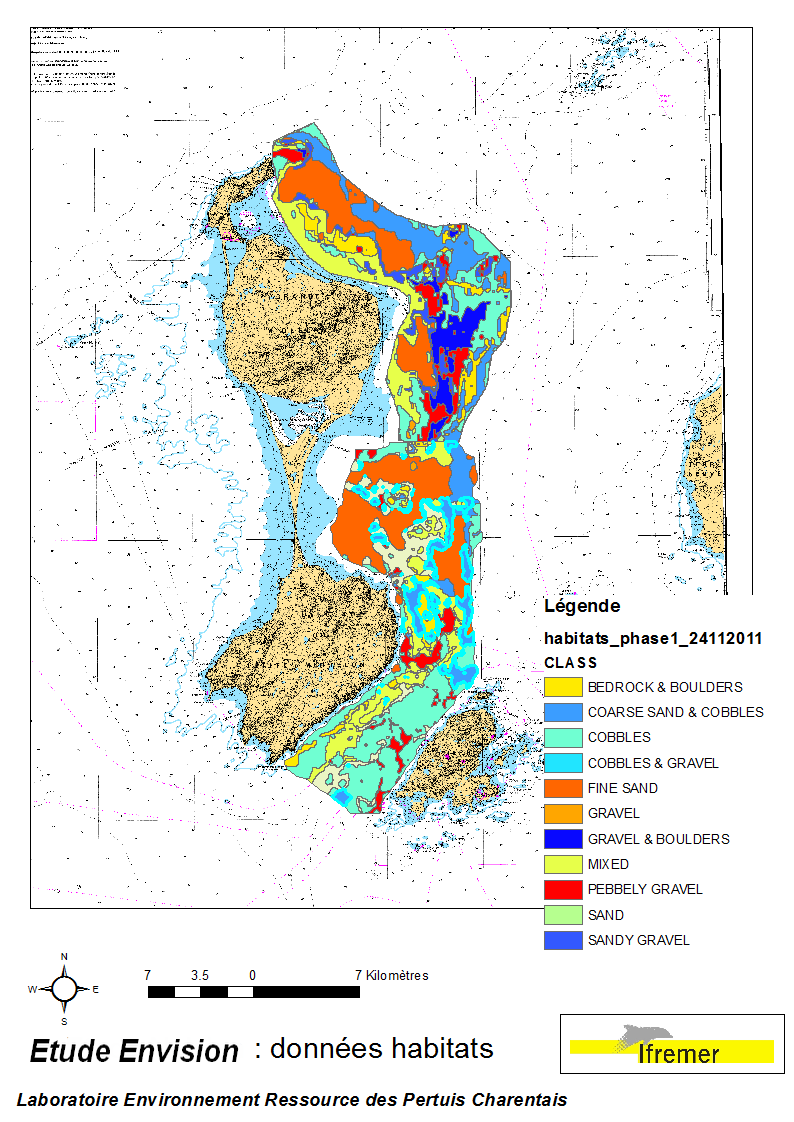
These data were collected during the 2007 and 2011 ENVISION-Ifremer campaigns to sustain a R & D project focusing on the Pectinid aquaculture development. This project was co-funded by the Saint Pierre et Miquelon public body and ODEADOM. This work aims to assess and select new potential rearing areas for the King scallop Placopecten magellanicus by using bottom type data resulting from 2 mapping campaigns carried out in 2007 and 2011 on the Eastern coast of Saint Pierre et Miquelon archipelago.
-
The mapping of habitats off the coast of Congo was carried out by the Ifremer Deep-Sea Laboratory as part of the ANR CONGOLOBE project (2011-2015, coordinator Christophe RABOUILLE). The method used for this habitat mapping is based on the preliminary analysis of images acquired with the ROV Victor 6000 during two oceanographic campaigns: WACS (from 26/01/2011 to 25/02/2011, mission chief: Karine OLU) and CONGOLOBE (from 11/12/2011 to 12/01/2012, mission chief: Christophe RABOUILLE). The habitats were described at the finest level of analysis and then classified according to the EUNIS typology (https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/data/eunis-habitat-classification-1). Data published in: Sen, A., B. Dennielou, J. Tourolle, A. Arnaubec, C. Rabouille and K. Olu (2017). Fauna and habitat types driven by turbidity currents in the lobe complex of the Congo deep-sea fan. Deep-Sea Research Part Ii-Topical Studies in Oceanography 142: 167-179. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr2.2017.05.009
-
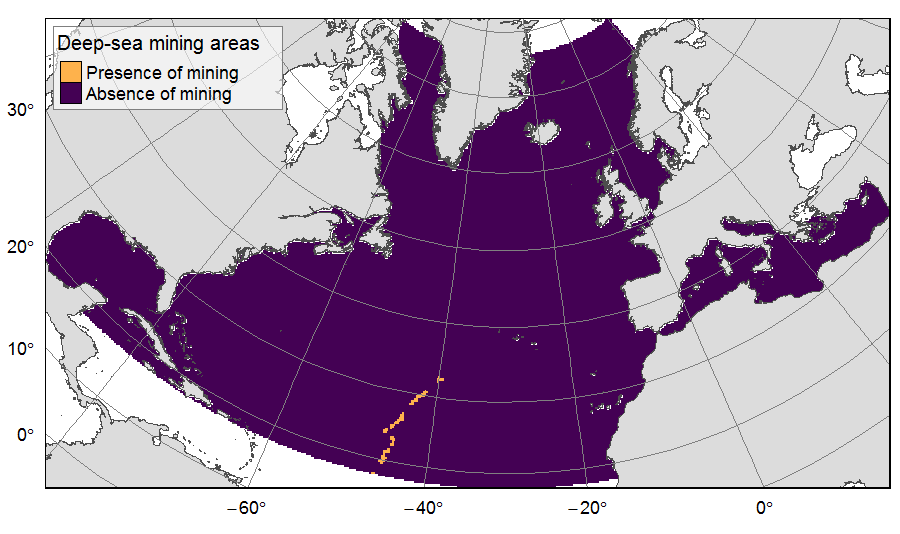
Presence of deep-sea mining exploration zones on the North Atlantic (18°N to 76°N and 36°E to 98°W). These areas correspond to the three polymetallic sulphides exploration contracts on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, attributed to Poland, France and Russia. Each of the three contract areas is divided into 100 squares of 10km by 10km. Source polygons originated from the International Seabed Authority. The presence (value=1) of deep-sea mining was extracted in 25km * 25km gridsquares. This dataset was built to feed a basin-wide spatial conservation planning exercise, targeting the deep sea of the North Atlantic. The goal of this approach was to identify conservation priority areas for Vulnerable Marine Ecosystems (VMEs) and deep fish species, based on the distribution of species and habitats, human activities and current spatial management.
 Mon GéoSource
Mon GéoSource