oceans
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
INSPIRE themes
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-
Suivi de contrôle réglementaire de la qualité des eaux de baignade sur la Côte basque. ARS
-

La campagne annuelle d'évaluation des ressources halieutiques PELMED (PELagiques MEDiterranée) est menée par le Laboratoire Halieutique Méditerranée de la station Ifremer de Sète. Les objectifs de ces campagnes sont : 1. Évaluer la biomasse des petits pélagiques (anchois, sardines) par méthode directe. Pour cela, la campagne doit alterner entre prospection acoustique et chalutages d'identification. Un signal acoustique est envoyé depuis un sondeur fixé sous le navire et chaque fois qu'il rencontre le fond ou des bancs de poissons, il est réfléchi et retransmis aux sondeurs. Ainsi, on peut observer en continu la forme et l'intensité de ces échos qui matérialisent les bancs de poissons. Des chalutages d'identification des espèces sont effectués afin de définir la proportion des espèces présentes dans les échos détectés. 2. Collecter le plus grand nombre de paramètres biologiques possible sur les espèces cibles de petits pélagiques (anchois, sardines, sprats) pour mieux comprendre la dynamique de population de ces espèces. Pour cela, des mesures morphométriques, ainsi que la détermination du sexe et du stade de maturité des poissons sont réalisées. Enfin, des otolithes sont prélevés afin de pouvoir déterminer l'âge des poissons. Ces paramètres biologiques sont très importants pour compléter l'évaluation de biomasse et avoir une meilleure compréhension des processus sous-jacents à la variabilité de ces populations. Cela permet par exemple de déterminer la structure en âge ou en taille des populations, d'avoir une idée de leurs réserves énergétiques, etc. 3. Mieux comprendre l'écosystème pélagique dans son ensemble, du plancton aux prédateurs supérieurs. La campagne PELMED a pour but premier d'évaluer les stocks de petits pélagiques, mais elle s'attache également à accumuler le plus de données possible sur les différents compartiments de l'écosystème pélagique, allant des paramètres physiques (température, salinité) aux prédateurs supérieurs (mammifères marins, oiseaux), en passant par les différents niveaux trophiques inférieurs (phyto- et zooplancton, poissons petits pélagiques). Ainsi, après chaque chalutage, une station hydrologique est réalisée avec la mesure de la température et de la salinité le long de la colonne d'eau via une CTD, des prélèvements d'eau et de phytoplancton avec une bouteille Niskin et des prélèvements de zooplancton à l'aide d'un trait vertical de WP2. Enfin, tout au long de la campagne nous réalisons l'observation et le comptage des oiseaux et mammifères marins. En plus de la compréhension de l'écosystème, ceci devrait permettre de fournir un certain nombre d'indicateurs nécessaires au suivi du milieu marin dans le cadre de la DCSMM (Directive Cadre sur le Milieu Marin).
-

Nos travaux ont pour objectif d’étudier la biogéochimie non stationnaire des sédiments intertidaux du Bassin d'Arcachon. Quatre stations caractéristiques des trois principaux types de sédiments intertidaux du bassin et favorables aux conditions transitoires sont échantillonnées depuis quelques années: 1) les sédiments sableux perméables dans le haut de plage (station 1/S); 2) les vases couvertes par Zostera noltii (station 3/VH), et 3) les vases nues (stations 2/VN et 4N marquées par des conditions redox différentes). Les questions fondamentales que nous souhaitons aborder dans ce travail concernent : i) l’influence des alternances émersion/immersion et jour/nuit sur les réactions biogéochimiques benthiques, et leurs influence sur les flux des composés biogéniques et de métaux traces ; ii) la dynamique biogéochimique et les processus spécifiques se déroulant dans les sédiments sableux perméables de la zone intertidal ; iii) la variabilité saisonnière de ces processus et le métabolisme net de ces environnements. Notre expertise repose sur l’utilisation d’outils in situ (voltammétrie, DET, profileur benthique) et ex situ (découpage et incubation de carottes).
-

Échantillonnage de l'eau de surface toutes les heures dans le Chenal de Teychan afin d'identifier les variations des paramètres bioogéochimique au cours d'un cycle nyctéméral (jour/nuit) et deux cycles de marée. L'échantillonnage est saisonnier. L'effet de la marée est plus important que l'effet jour/nuit sur les variations des paramètres mesurés.
-

Les signatures élémentaires, isotopiques et biochimiques du sédiment des 6 stations benthiques de suivi sont analysées selon la découpe suivante: 0-0,5 / 0,5-1 / 1-2 / 2-3 / 3-5 / 5-7 / 7-10 cm
-

L’étude avait pour but de connaître la signature élémentaire et isotopique des différentes sources potentielles de la Matière Organique Particulaire (MOP) du bassin d’Arcachon. Pour ceci a été analysée la MOP du bassin ainsi que ses sources potentielles (les macro-algues, les végétaux supérieurs, les sédiments et les sols des différentes stations de prélèvement). La contribution de chacune de ces sources a ainsi été quantifiée.
-
L'origine de la matière organique particulaire (MOP) et le réseau trophique pélagiques et benthiques ont été étudié à l'aide d'analyses élémentaires et isotopiques. Les principales sources de MOP soutenant l'activité biologique ont été déterminées.
-

Un échantillonnage mensuel, de la colonne d'eau (en surface) de la Leyre au pont de Lamothe, est effectué afin de mesurer la variation de la qualité de la matière organique particulaire d'origine continentale.
-
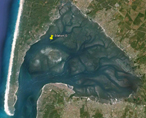
Un échantillonnage bi-mensuel, à la station G, de la colonne d'eau (à pleine mer, en surface) est effectué afin de déterminer la qualité et l'origine de la matière organique particulaire. Cet échantillonnage est effectué en supplément de celui réalisé dans le cadre du SOMLIT (Service d'Observation en Milieu LITtoral) aux stations Bouée 13, Tès et Comprian.
-
Etude Bidur / Lorea
 Mon GéoSource
Mon GéoSource